Hearing Loss Information
Hearing loss, ranging from rapid to progressive decline and temporary to permanent, can be mild to profound. It is categorized by damage: conductive, sensorineural, or mixed.
Types of Hearing Loss
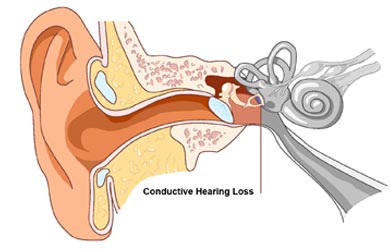
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss results from inefficient sound conduction through the outer ear canal to the eardrum.
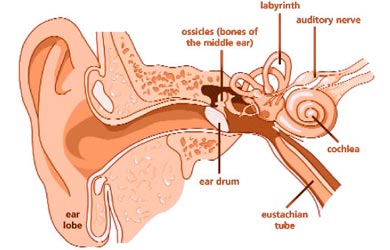
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural auditory impairment, characterized by damage to the auditory nerve, is the prevalent form of hearing loss.
Combined Hearing Loss
Combined hearing loss involves both conductive and sensorineural components
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound is not conducted efficiently throught the outer ear canal to the eardrum and the tiny bones, or ossicles, of the middle ear. Conductive hearing loss usually involves a reduction in sound level,or the ability to hear faint sound. A conductive hearing loss is a hearing loss where the ears ablility to conduct sound into the inner ear is blocked or reduced. A conductive hearing loss affects the passage of sound between the ear drum and the inner ear. Conductive hearing loss is the result of sounds not being able to pass freely to the inner ear.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural loss is the most common type of hearing loss. A sensorineural hearing loss is defined as damage to the hair cells in the cochlea (this is the sensory hearing organ) or damage to the neural pathways of hearing (nerves). This type of hearing loss occurs when the inner ear or the actual hearing nerve itself becomes damaged. This loss generally occurs when some of the hair cells within the cochlea are damaged.
Combined Hearing Loss
Combined hearing loss describes the occurrence of conductive hearing loss that also has a sensorineural component.Mixed hearing loss occurs when there is a combination of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. People may have a sensorineural hearing loss and then develop a conductive component in addition to their original loss.
Symptoms of Hearing Loss
The symptoms of hearing loss can vary from type, cause, and degree of loss.
Difficulty understanding everyday conversation

Having to turn up the TV or radio

Avoidance of social situations that were once enjoyable

A feeling of being able to hear but not understand
Asking others to repeat often

Tinnitus, or ringing and/or buzzing sounds in the ears

Increased difficulty communicating in noisy situations like restaurants, group meetings

Muffling of speech and other sounds.
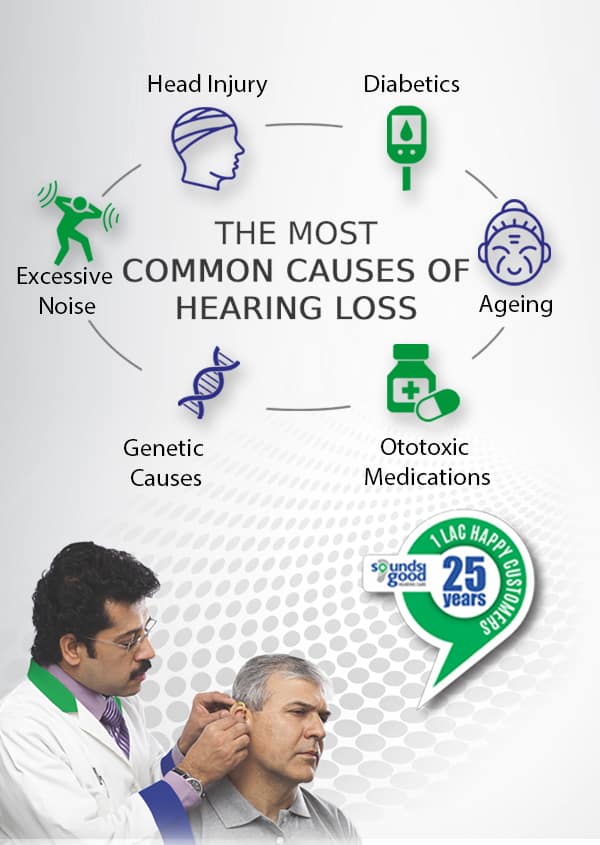
Hearing Loss Causes
The cause is crucial to understand as it affects the determination of right treatment. Certain types include:
Hearing Loss Causes
The cause is crucial to understand as it affects the determination of right treatment. Certain types include:

Certain Medications

Trauma Or Injury To The Head

Prolonged Exposure To Excessively Loud Noise

A Single Episode Of Acoustic Trauma

Certain Illnesses Such As Mumps, Meniere’s Disease, Otosclerosis Or Autoimmune Disease

A Tumor On The Acoustic Nerve Or Acoustic Neuroma
FAQ - Hearing Loss
What are the different types and styles of hearing aids?
Today’s hearing aids are smaller and designed to be discreet. Many are nearly undetectable even close up. One model actually sits completely in the canal of your ear and is practically invisible when worn. Alternately, fashionable, meant-to-be seen hearing aids in fun color combinations and exotic flowery flourishes are available.
What are the most common hearing loss causes?
There are several causes. The main ones include excessive noise, infections, genetics, birth defects, infections to the head or ear, aging, and reaction to drugs or cancer treatment.
Wouldn’t I already know if I had hearing loss?
Few physicians routinely screen for hearing loss. Since most people with hearing impairments hear fine in quiet environments, it can be a very difficult problem for your doctor to recognize.
Doesn't hearing loss only affect old people?
Hearing loss can occur at any time, at any age. In fact, most people with hearing loss (65%) are younger than age 65! There are six million people in the U.S. ages 18-44 with hearing loss, and around one-and-a-half million are school age.
How do I know hearing aids will work for me?
Consumers relish a 30-day trial period for hearing aids, during which the hearing care experts guarantees satisfaction through periodic checks and modifications.






